Introduction to Business Management - Final
History of Business
Pre Industrial
During this time, most business was dependent on transport by sea or land. With the rise of the industrial revolution, came an increase in manufacturing. This prompted the introduction of bonds and trusts. Bonds made trading much easier and more efficient. Trusts were a way to pool money together to invest in a business. This allowed for more people to invest in a business and made it easier to raise capital. This also allowed for the creation of stock exchanges.
As the world grew in complexity, a demand for managers arose. This led to the creation of management schools.
Basic Concepts of Business
The foundation of conducting business is supply and demand. Business can be conducted in various markets, some of which include:
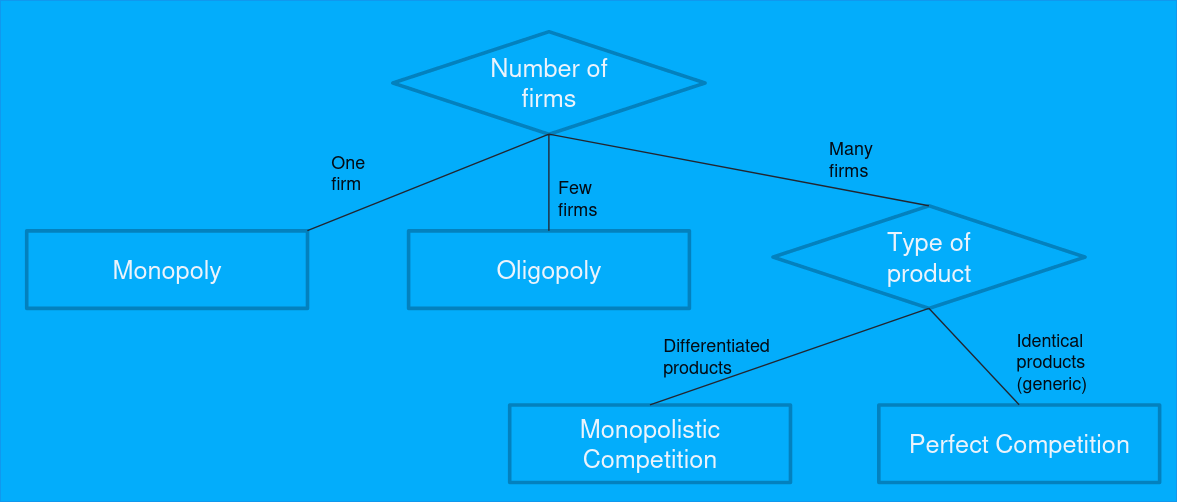
- Monopoly
- This is a kind of market with a single seller.
- Oligopoly
- In this market, there are a few sellers.
- Monopolistic Competition
- Here there are many unique sellers.
- Perfect Competition
- This is a market with many sellers, all of which sell identical products.
Demand Curve
For an increase in price, there will be an increase in quantity. The key definition here is that the demand implies an indirect relationship between price and quantity.
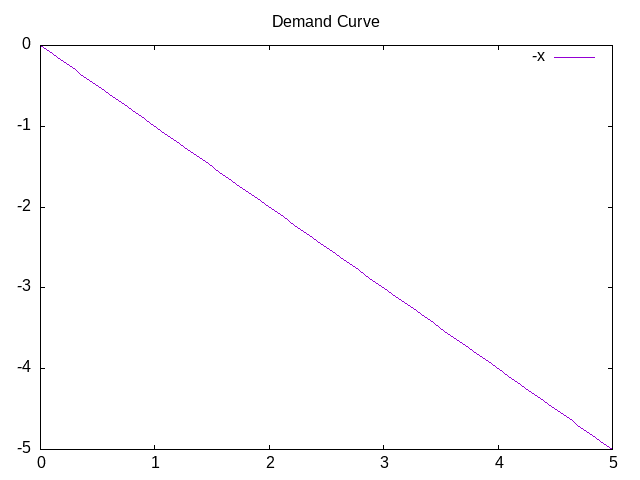
What might cause the demand curve to shift? There are a few things that can cause the demand curve to shift. These include:
- Change in the in come of the consumer
- Change in the price of related goods
However, there is an exception for inferior goods. For inferior goods, a decrease in income will cause an increase in demand. This is because the consumer will be more likely to purchase the inferior good.
Supply Curve
Inverse to the demand curve, the supply curve implies a direct relationship between price and quantity. For an increase in price, there will be a decrease in quantity. What might cause the supply curve to shift? There are a few things that can cause the supply curve to shift. These include:
- Change in COP - New technology
- Change in the price of related goods
- Change in the price resources
Equilibrium
This is the intersection of the supply and demand curves. This is the point where the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied. This is the point where the price is at its lowest and the quantity is at its highest. This is the point where the market is most efficient.
If at any point the price is above the equilibrium, there is surplus in the market, and vice versa, there is a shortage in the market.
Cost of Production
The cost of production is the cost of producing a good or service. This includes the cost of the labor, the cost of the raw materials, and the cost of the capital. There are two types views for costs:
| Economic View | Accountig View |
|---|---|
| Economic Profit | Accounting Profit |
| Economic Cost | Accounting Cost |
| Implicit Cost |
Law of Diminishing Return
Each type of production has some optimal levels, if this level is exceeded, the the cost of producing more units grows as well.
Economic Theories and Business
The study of economics is the study of how people make decisions. There are two main theories of economics: classical and keynesian.
Classical Economics
This theory is based on the idea that the market is self-regulating. The man behind this theory is Adam Smith.
As the 1929 depression struck, it was clear that the classical theory was not working. This led to the creation of the keynesian theory.
Keynesian Economics
This theory relies on the fact that the government should interfere in the market in order to regulate it.
Market Structures
There are four main market structures: monopoly, oligopoly, monopolistic competition, and perfect competition.
Competitive Strategy
Industry Evolution
Evolution of an industry is a result of innovation. The three key stages are: Variation, Selection, and Retention.
- Variation
- In this stage, a new product is created.
- Selection
- Now the product is tested (in the market) to see if it is successful.
- Retenation
- At this point, the new product that has been tested is being sold on the market.
Disruption
Disruption comes when a new technology is introduced. This technology should be something which creates more value for the customer. This change causes a drastic shift in the market. This is not only the result of innovative disruption, it could also be a change in leadership. It could also be a change in the architecture of a business.
- How do we disrupt
- We combine similar elements in a different way and introduce new elements.
Incumbents are firms who ignore the disruption and continue to do business as usual. Disruptors are firms who take advantage of the disruption and change their business model.
Strategy
Strategy is about winning in the market. The goal of a successful strategy is to create a sustainable competitive advantage. This means that we are able to grow more than our competitors. This is done by creating a unique value proposition.
We will also look at the blue ocean strategy.
Strategy can be done on two levels:
- Corporate Level Strategy :: Here we decide in which markets we want to compete. How we want to diversify, integrate and expand. (What investors are interested in)
- Business Level Strategy :: Here we decide how we want to compete in the market. We strive to find the competitive advantage. (
Economic Logic
The economic logic is the value proposition of the business. This is the value that the business creates for the customer. This is the value that the customer is willing to pay for. This is the value that the business is able to capture.
This is a way of providing that unique value proposition. It focuses on four key elements:
- Phases :: How do we plan our the project? What are the phases of the project?
- Places :: Where will we sell? Who will we sell to?
- Differentiators :: What makes us different? What is our competitive advantage?
- Vehicles :: How will we get to where we need to be?
Strategy Archetypes
There are four main strategy archetypes: cost leadership, differentiation, focus. and stuck in the middle. These are based on the economic logic. The cost leadership strategy is based on the lowest cost. The differentiation strategy is based on unique value proposition. The focus strategy is based on specialization. The stuck in the middle strategy is based on average cost.
- Cost Leadership
- Our goal here is to minimize our costs. We can achieve this by economies of scale, economies of learning, production techniques, material costs, utilizing capital, efficiency.
- Differentiation
- We want to create a unique value proposition. We can differentiate by having more attractive cost leadership, this means we price our product lower than our competitors. Some more sources of differentiation are: product performance, complementary services, company procedures, localization, vertical integration.
- Focus
- We want to find a very specific market.
Strategy Formulation
There are three main steps in strategy formulation:
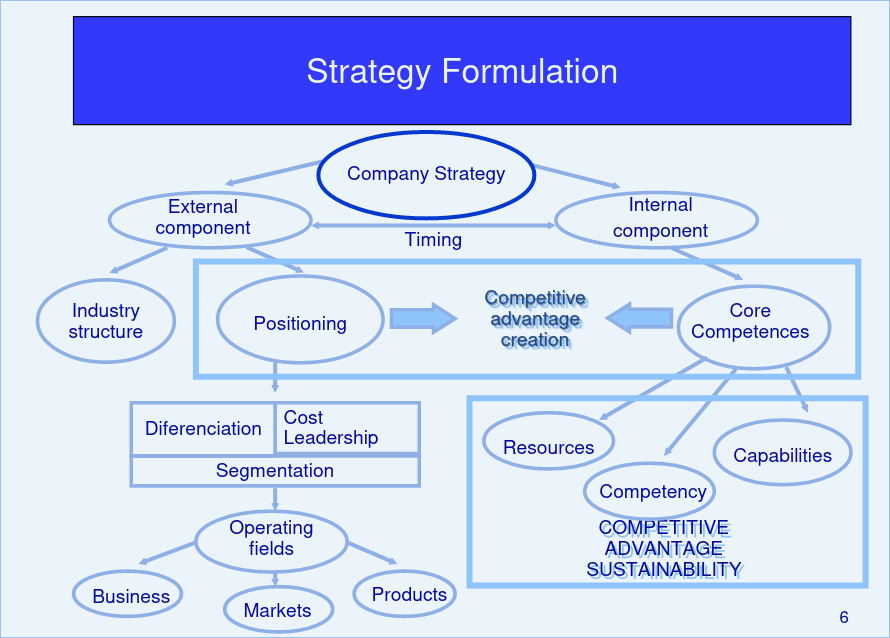
Strategy Development
There are three main steps in strategy development:
- Sector Understanding (SWOT, 5 forces, etc.)
- Positioning (Value Chain, Value Network, etc.)
- Resource Development
Finding your place: If you cannot compete with the current market, you may want to consider creating a new market. This is called blue ocean strategy.
Blue Ocean Strategy
This is a strategy where you create a new market. This is done by creating new demand. By doing this, you:
- Make competitors irrelevant
- Differentiating costs
- No competition
What is very useful to do when creating a blue ocean is the strategy canvas. This is a tool that helps you to create a new market. It is based on the value innovation principle.
The following is an example for video streaming services:
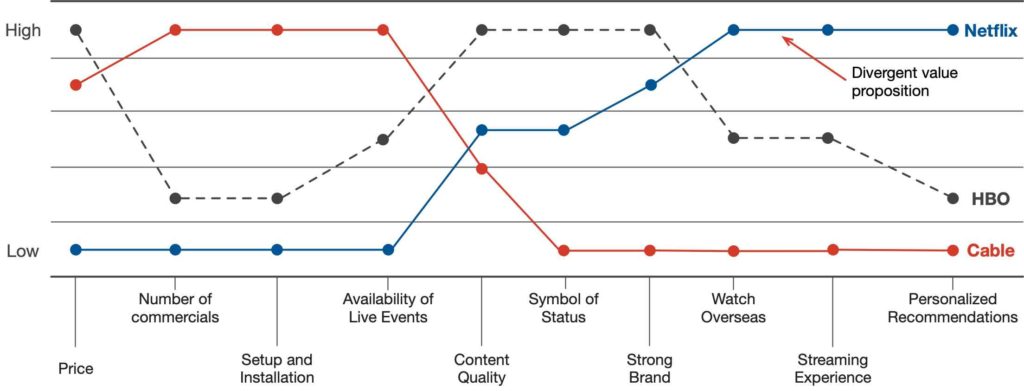
The four key steps in creating a blue ocean strategy are:
- Eliminate
- Increase
- Reduce
- Create
Business Analysis Tools
SWOT Analysis
This is a tool which we can use to analyze a company. It relies on four key elements: strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
It is usually done by looking at the internal and external environment of the company and analyzing the negative and positive parts. Here is the SWOT matrix:
| Internal Factors | External Factors | |
|---|---|---|
| Positive | Strengths | Opportunities |
| Negative | Weaknesses | Threats |
Porter's Five Forces
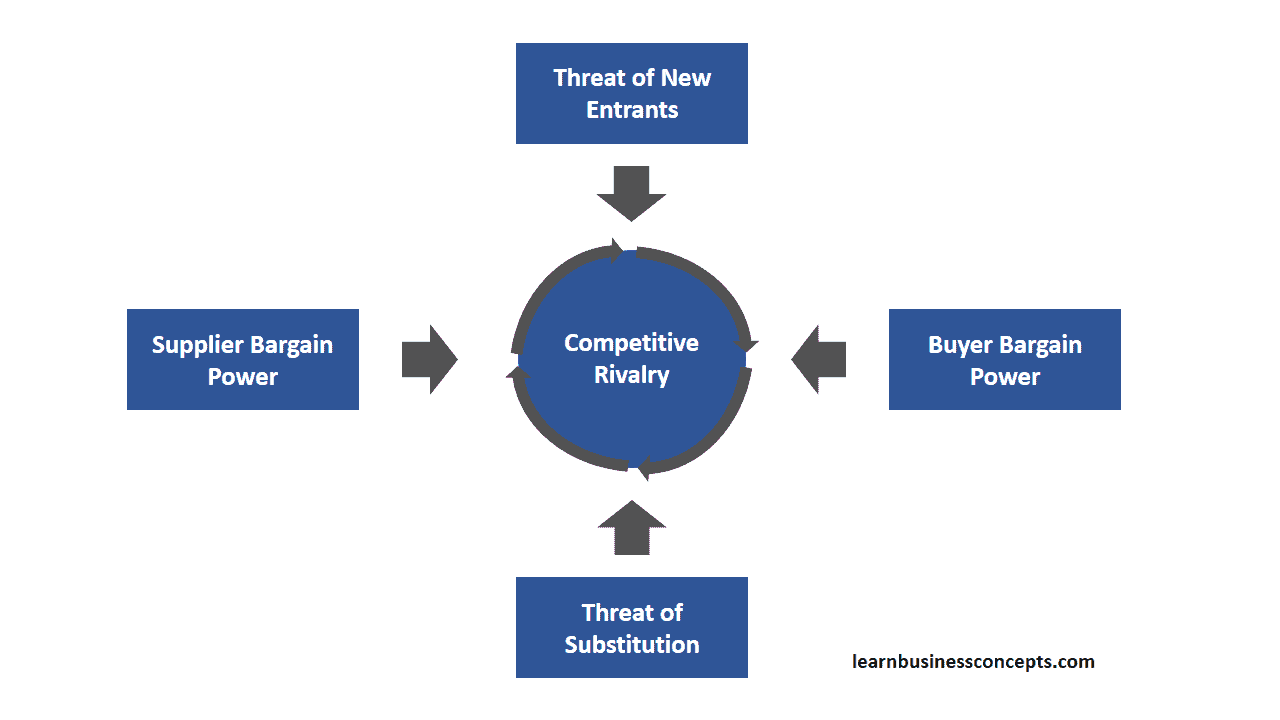
How does this model work? It considers each of the forces, and determines the vulnerability or strength of the company.
- Threats of new enterants
- This force considers the possible threat of new companies entering the market. What this is based on, is the entry barriers for the given market.
- Buyer Bargain Power
- For this force, we determine consider the number of buyers and the importance of the buyers. From this, we can determine the bargaining power of the buyers.
- Supplier Bargain Power
- For this force, we determine consider the number of suppliers and the importance of the suppliers. From this, we can determine the bargaining power of the suppliers.
- Threat of Substitutes
- This force considers the threat of substitutes in the market. This is done by looking at the substitutes, switching costs, and buyer information.
MOST Analysis
This is a tool which we can use to analyze a company. It relies on four key elements: Mission, Objectives*, strategy, and Tactics.
- Mission
- The purpose and definition of the company.
- Objectives
- The goals of the company. We must be able to measure these.
- Strategy
- The way we are going to achieve our goals. We should be able to track this.
- Tactics
- Next steps for implementing our strategy.
Here is an example of a MOST analysis for Google:
- Mission
- To organize the world's information and make it universally accessible and useful.
- (no term)
- Objectives
- To provide the best search engine.
- To provide the best advertising platform.
- To provide the best cloud computing platform.
- (no term)
- Strategy
- Search Engine
- To provide the best search engine, we will use machine learning to improve our search engine.
- Advertising Platform
- To provide the best advertising platform, we will use machine learning to improve our advertising platform.
- Cloud Computing Platform
- To provide the best cloud computing platform, we will use machine learning to improve our cloud computing platform.
- (no term)
- Tactics
- Search Engine
- We will use machine learning to improve our search engine.
- Advertising Platform
- We will use machine learning to improve our advertising platform.
- Cloud Computing Platform
- We will use machine learning to improve our cloud computing platform.
Creation
Value Chain
It is a chain which describes the process from the point of gathering resources all the way to selling the product. What makes this important is that it helps us identify our primary and secondary (support) activities.
Business Process Modeling and Re-engineering
All companies will reach points when they have to re-engineer their business processes. This is because the world is changing, and the company needs to adapt to the changes. BPR makes a company undergo drastic changes, hoping to improve: quality, output, costs, service and speed.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
This is a digital system which improves the functioning of a company by: imporving communication, improving efficiency, and improving productivity. It is a system which helps a company to manage its resources.
Business Growth
Product Life Cycle
This is a cycle which describes four distinct stages of a product. These are: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline.
- Introduction
- You try to educate the market about your product.
- Growth
- Now that people, know about your product, you try to increase your sales. You are also trying to build brand loyalty.
- Maturity
- Given that you now have loyal customers and a successful product, you to try to maintain your sales. You might also try to improve your product.
- Decline
- Now the market has become a lot more saturated, and your product is starting to lose its appeal. You might try to re-invent your product, or phase it out. The key part of this stage is that you try to milk your brand, and get as much money as you can.
BCG Matrix
With this model, we can correlate the different stages of the product life cycle with how market growth and market share are changing.

A key takeaway from this is that if you have a product which is in the cash cow stage, you should invest the money into a question mark product. This is because the cash cow product is in the decline stage, and you should try to phase it out.
Ansoff Matrix
This is a model which can help us analze our strategy for growing.
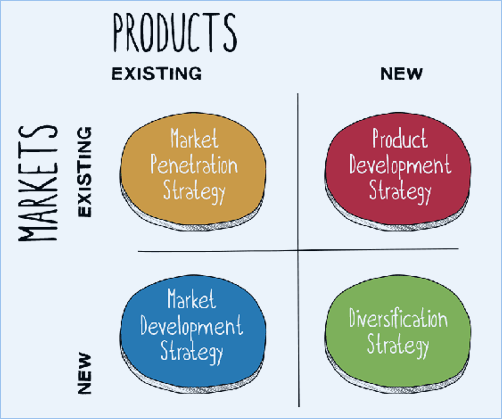
We can look at the market and the product to determine the strategy. It is also important to try to make the business as synergetic as possible.
Vertical & Horizontal Integrations
- Vertical Integration
- A process of taking up more space in the chain. This can be done by buying the company which either provides some resources or sells the product.
- Horizontal Integration
- Here we try to occupy more space on the same level of the chain. This can be done by buying a company which is in the same stage of the value chain. The key objectives here are to increase the control of the company, and to increase the synergy of the company.
Make or Buy
It is not necessary to always make everything yourself, you can outsource a lot as a company. The key decision is to make sure your core competencies are not being outsourced.
Business Models
B2B
B2C
C2C
Business Decision Making
Data Driven
Balanced Scorecards
Strategy Implementation
Organization
Processes
People
Culture
Organizational Structure and Design
Formal & Informal Structures
Approaches
Functional
Divisional
Matrix
Team & Networking
Cultural Management
Cultural Dimension Models
Corporate Governance
The C-Suite
The Board
The Shareholders
Public & Private Enterprises
RDI
Objectives
Structure
Roles
Finance
Objectives
Structure
Roles
Legal
Objectives
Structure
Roles
Sales & Marketing
Objectives
Structure
Roles
IT Department
Objectives
Structure
Production Operations
Objectives
Structure
Human Resources
Objectives
Structure
Roles
Scalability & Growth
Key Difference
International Strategies
Asset Heavy & Asset Light
SASS Scaling
Glocal Companies
Local + Global
Act Global
Think Global
Adaptation
What to do?
Internalization
Market Research
Commercial Missions
Partnerships
Sample Quiz
- What is the most important factor to consider when developing a business plan?
- Cost
- Market
- Competition
- Strategy
- Which of the following is NOT an example of a business resource?
- Office supplies
- Human capital
- Technology
- Natural resources
- What is the definition of a sole proprietorship?
- A business owned by multiple people
- A business owned by a single person
- A business owned by a corporation
- A business owned by the government
- What is the primary goal of a business?
- To make a profit
- To provide employment
- To satisfy customers
- To become a global leader
- What are the four main functions of management?
- Planning, organizing, leading, and controlling
- Planning, hiring, leading, and controlling
- Planning, organizing, motivating, and controlling
- Planning, organizing, leading, and motivating
- What is the purpose of a mission statement?
- To define a company's goals and objectives
- To define a company's values and beliefs
- To define
a company's competitors
- To define a company's products and services
- What is the difference between a manager and an entrepreneur?
- A manager is responsible for managing the operations of a business, while an entrepreneur is responsible for creating and growing a business.
- A manager is responsible for creating and growing a business, while an entrepreneur is responsible for managing the operations of a business.
- A manager is responsible for managing the finances of a business, while an entrepreneur is responsible for creating and growing a business.
- A manager is responsible for creating and managing a team, while an entrepreneur is responsible for managing the finances of a business.
- What is the purpose of a SWOT analysis?
- To evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of a business
- To evaluate the success of a business
- To evaluate the competition of a business
- To evaluate the market of a business
- What are the three main types of business organizations?
- Sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations
- Franchises, partnerships, and corporations
- Sole proprietorships, franchises, and partnerships
- Sole proprietorships, limited
Now create a free response question to sum up the entire year of learning:
- In your own words, explain the importance of business management and why it is essential for businesses to succeed.